
H.265: The new image compression format
 Recently, the ITU-T Video Coding Experts Group (VCEG) developed the H.265 standard, also called HEVC (High Efficiency Video Coding), successor of H.264 - which has dominated the market in the last 5 years.
Recently, the ITU-T Video Coding Experts Group (VCEG) developed the H.265 standard, also called HEVC (High Efficiency Video Coding), successor of H.264 - which has dominated the market in the last 5 years.
H.265 is a video compression format two times more efficient than its predecessor; it uses only 50% of the bandwidth, while maintaining the same quality as H.264.
It supports 4K (4096 x 2160) content and even 8K (8192 x 4230), also called the UHD, which makes it the ideal technology for transmitting images from megapixel cameras .
While H.264 can transfer HD images using a 1Mbps bandwidth, H.265 can transfer Full HD content using the same bandwidth.
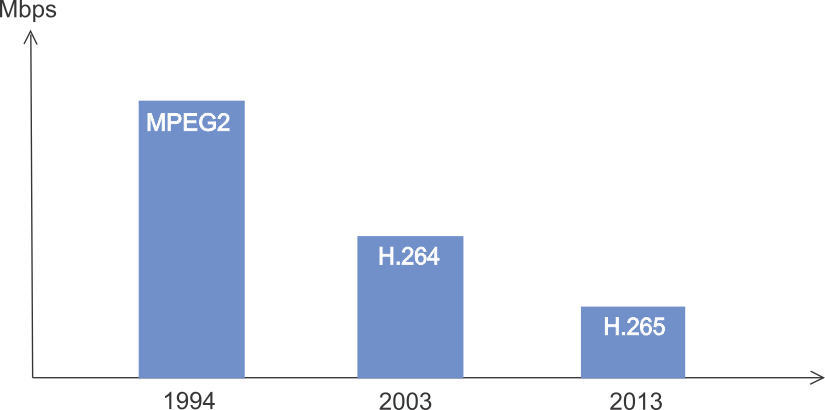
Video codecs evolution
At approximately every 10 years a new generation of video compression format has made the bandwidth drop by half while maintaining the same image quality.
Why H.265 is more efficient?
Like its predecessor, H.265 is also based on the same principle of frame comparison.
Similar pixels between the previous and the current frame, i.e. parts of the image where there is no motion is subtracted from the current frame and the rest is mathematically transformed, thus reducing the amount of data required to store each data frame.
When a frame is H.264 encoded, it is divided into several squares, known as macroblocks , that are no larger than 16 x 16 pixels, very small for HD or Ultra HD images. H.265 allows blocks up to 64x64 pixels and that's the main difference between the two formats.
To explain this better, take a look at the two images below:
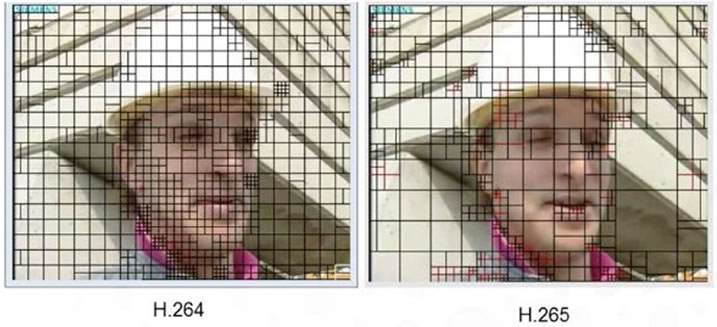
Source: Elemental technologies
Note that image on the left, where it was applied H.264, has much more macroblocks than image on the right, because H.265 format could use larger blocks (up to 64x64) in areas where pixels have the same color or no change.
The fact that an area of 64 x 64 pixels can be stored in only one macroblock in H.265 format, while the same area needed four 16x16 pixel macroblocks in H.264, proves that H.265 compression is more efficient.
Total compression process is a bit more complicated than that. There are many other factors to consider, which will not go on merit here not to make this a too complex and boring article.
My intention was to give a sense of basic differences between these two formats, just enough to be able to demonstrate how H.265 compresses data better than H.264.
With H.265 popularization, soon we'll be able to watch Full HD images of a security system in our smart phones and tablets.
H.26x type video CODECs aren't suitable for CCTV purposes?
MPEG group, who developed H.264 and H.265 video codecs, already made it clear that they have not been developed for CCTV applications. They said that H.264 was developed at the request of Steven Spielberg to be applied in the entertainment industry .
It is this argument that some manufacturers use to justify the use of a proper CODEC that, according to themselves , it would be more efficient than H.264.
The problem with these MPEG codecs is that they capture a full frame every n frames and frames in between are filled with only the difference between them and the last full frame, until a new full frame is captured .
Also according to these manufacturers, it would be problematic if an event occurrs between two full frames, exactly when one of these intermediate frames is being captured.
Aug/2014
Nov/2015
Wanna know when new articles will be published?
Like this article? Leave a comment!
Copyright ©2014 CCTV Institute- All rights reserved
Total or partial reproduction of any content in this website is forbidden except if expressly authorized by the author




